Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Previous issues
Review Articles
- A Scoping Review of Clinical Research on Motion Style Acupuncture Treatment
- Doori Kim, Yoon Jae Lee, In-Hyuk Ha
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(2):65-76. Published online June 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.06.001
- 1,739 View
- 42 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 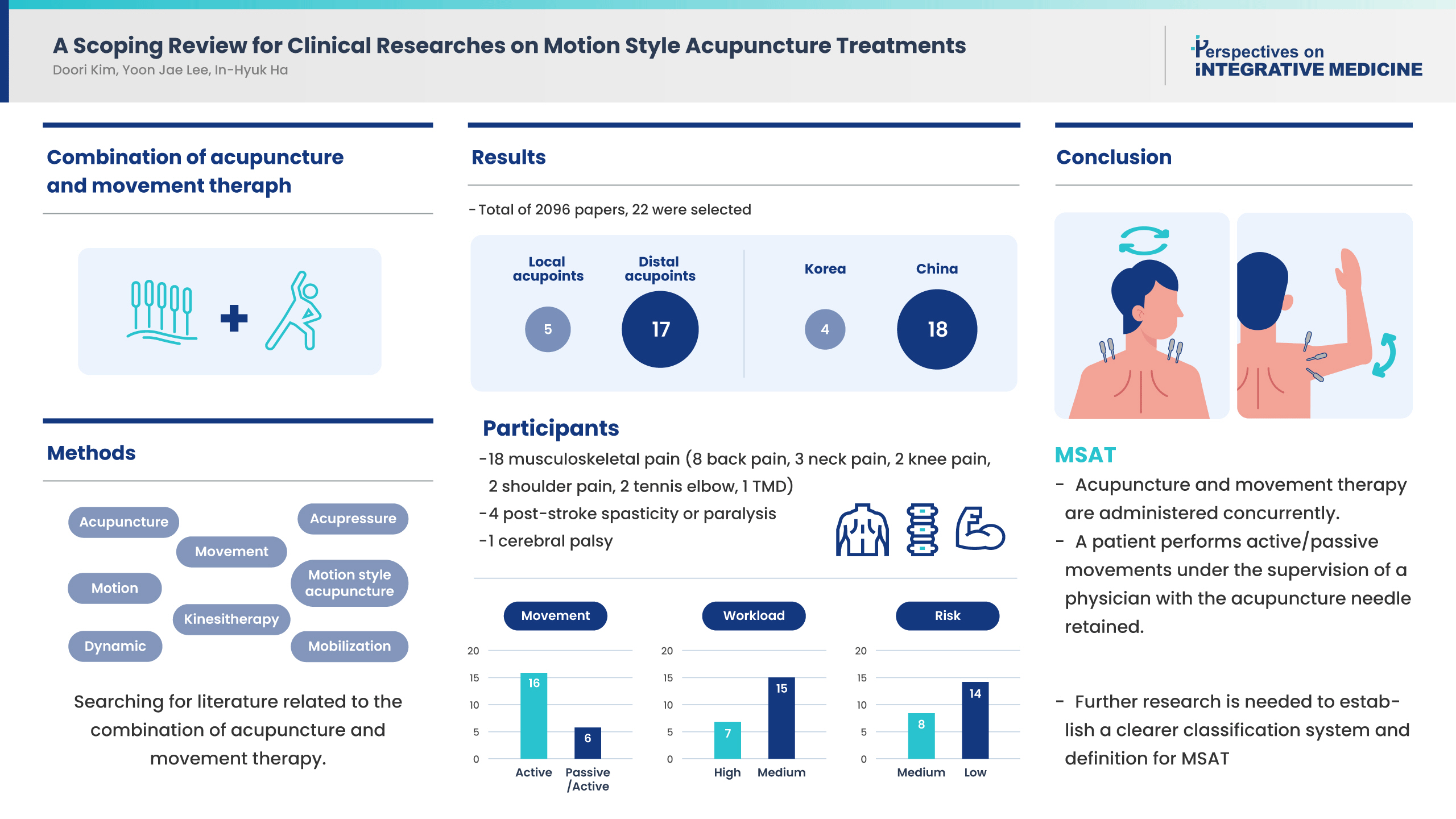
- This scoping review was conducted to examine the concept of Motion style acupuncture treatment (MSAT), use in clinical practice, its effectiveness, and safety. A literature review of clinical study treatment methods combining acupuncture and movement therapy was performed using PubMed. Of 2,096 studies retrieved, 22 were included in this review. There were 12 randomized controlled trials, and all 22 studies were published in China and Korea, mostly, within the last 3 years. There were five studies concerning local acupoints and 17 studies regarding needling at distal acupoints, and the level of risk of the procedure was “high” in eight studies and “moderate” in 14 studies. The study participants were patients with musculoskeletal pain, and many studies reported significant improvements in pain and functional disability outcomes following treatment using MSAT. For conclusion, MSAT refers to a treatment method in which a patient performs active/passive movements under the supervision of a physician with the acupuncture needle retained at the insertion site. However, there are a limited number of MSAT studies, and various treatment types and related terms are mixed. Further studies, classification of the types of MSAT using a well-established classification system, and a clearer definition of the MSAT concept are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of lumbar motion style acupuncture treatment on inpatients with acute low back pain: A pragmatic, randomized controlled trial
Oh-Bin Kwon, Dong Wook Hwang, Dong-Hyeob Kang, Sang-Joon Yoo, Do-Hoon Lee, Minjin Kwon, Seon-Woo Jang, Hyun-Woo Cho, Sang Don Kim, Kyong Sun Park, Eun-San Kim, Yoon Jae Lee, Doori Kim, In-Hyuk Ha
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2024; 82: 103035. CrossRef - Effectiveness and Safety of Progressive Loading–Motion Style Acupuncture Treatment for Acute Low Back Pain after Traffic Accidents: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Seung-Yoon Hwangbo, Young-Jun Kim, Dong Guk Shin, Sang-Joon An, Hyunjin Choi, Yeonsun Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, Ju Yeon Kim, In-Hyuk Ha
Healthcare.2023; 11(22): 2939. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of lumbar motion style acupuncture treatment on inpatients with acute low back pain: A pragmatic, randomized controlled trial
- A Review of Major Secondary Data Resources Used for Research in Traditional Korean Medicine
- Chunhoo Cheon, Bo-Hyoung Jang, Seong-Gyu Ko
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(2):77-85. Published online June 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.06.002
- 1,126 View
- 23 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Research in health care using secondary data is steadily increasing worldwide. In this study, secondary healthcare data was reviewed, so that the information can potentially be used for Korean medicine research. The characteristics of the data, including the variables related to Korean medicine and the method of obtaining data, were summarized. The Korean medicine variables were extracted from the Korean Medicine Utilization Survey, Korea Health Panel, Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, Medical Service Experience Survey, and the health insurance claims data. Except for health insurance claims data, the data was obtained through relatively simple procedures. There were differences in the characteristics of each secondary data and the extent to which it was used in Korean medicine research. Many Korean medicine studies using secondary data will be conducted in the future and researchers must understand the characteristics of the data and analyze it appropriately.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Real-world data analysis on effectiveness of integrative therapies: A practical guide to study design and data analysis using healthcare databases
Ye-Seul Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, In-Hyuk Ha
Integrative Medicine Research.2023; 12(4): 101000. CrossRef - Trends in the treatment of fibromyalgia in South Korea between 2011 and 2018: a retrospective analysis of cross-sectional health insurance data
Jin-Sil Yu, Eun-San Kim, Kyoung Sun Park, Yoon Jae Lee, Yeon Cheol Park, Dongwoo Nam, Eun-Jung Kim, In-Hyuk Ha
BMJ Open.2023; 13(12): e071735. CrossRef
- Real-world data analysis on effectiveness of integrative therapies: A practical guide to study design and data analysis using healthcare databases
- Minimum Clinically Important Difference for Nonsurgical Interventions for Spinal Diseases: Choosing the Appropriate Values for an Integrative Medical Approach
- Ye-Seul Lee, Sungmin Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, In-Hyuk Ha
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(2):86-99. Published online June 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.06.003
- 727 View
- 26 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- The minimal clinically important difference (MCID) plays a crucial role in the design and interpretation of clinical trials, as it helps in distinguishing between statistically significant and clinically meaningful outcomes. This scoping review aims to collate and appraise the current research concerning the validation of MCIDs for surgical and nonsurgical measures for spine disorders. Two databases of MEDLINE (PubMed and EMBASE) were searched. There were 1,590 studies retrieved and 79 were selected as eligible for review. Measurement tools such as the Oswestry Disability Index, Neck Disability Index, Numeric Rating Scale, and Visual Analogue Scale were assessed by regions and interventions. A total of 24 studies identified MCIDs on nonsurgical interventions, and 55 studies identified MCIDs on surgical interventions. The range of MCIDs varied greatly depending on study population, specific interventions, calculation methods, and outcomes. This scoping review emphasizes the complexity and variability in determining MCIDs for musculoskeletal or neurodegenerative spinal diseases, influenced by several factors including the intervention type, measurement tool, patient characteristics, and disease severity. Given the wide range of reported MCIDs, it is crucial to consider the specific context when interpreting these values in clinical and research settings. To select an appropriate MCID value for comparison in a clinical trial, careful consideration of the patient group, intervention, assessment tools, and primary outcomes is necessary to ensure that the chosen MCID aligns with the research question at hand.
Guideline
- ACURATE: A Guide for Reporting Sham Controls in Trials Using Acupuncture
- Ye-Seul Lee, Song-Yi Kim, Hyangsook Lee, Younbyoung Chae, Myeong Soo Lee
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(2):100-106. Published online June 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.06.004
- 1,125 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This paper presents the Acupuncture Controls gUideline for Reporting humAn Trials and Experiments (ACURATE) checklist, an extension of The Consolidated Standards for Reporting of Trials (CONSORT) and to be used along with STandards for Reporting Interventions in Clinical Trials of Acupuncture (STRICTA) when both real and sham acupuncture needles are used in the study. This checklist focuses on a clear depiction of sham needling procedures to enhance replicability and enable a precise appraisal. We encourage researchers to use ACURATE in trials and reviews involving sham acupuncture to assist reporting of sham acupuncture procedures and the related components.
Original Articles
- Bojungikgi-tang Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses in RAW264.7 Macrophages and C57BL/6 Mice
- Hyo In Kim, Yohan Han, Jinbong Park
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(2):107-116. Published online June 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.06.005
- 823 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study evaluated the anti-inflammatory effect of Bojungikgi-tang (BJT) in a model of acute lung injury (ALI) in mice.
Methods
Murine cell line macrophages (RAW264.7) were treated with BJT for 30 minutes before lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment. The levels of cytokines, mRNAs, proteins, and related markers were investigated. In addition, BJT (200 mg/kg/day) was administered orally to C57BL/6 mice for 2 weeks prior to an intraperitoneal injection with LPS to induce sepsis and ALI; 24 hours post LPS injection, mice were sacrificed and blood was collected from the infraorbital vein. Lung tissue was harvested, hematoxylin and eosin staining was performed, the wet/dry ratio of the lung tissue was measured, and the serum cytokine levels were analyzed.
Results
Compared with LPS treatment, BJT suppressed LPS-induced mRNA expression and secretion of inflammatory cytokines in RAW264.7 macrophages. Furthermore, inducible nitric oxide synthase, cyclooxygenase-2, toll-like receptor 4, phosphorylation of mitogenactivated protein kinases, and phosphorylation of nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells were inhibited by BJT. In mice, LPS-induced pathological changes in lung tissues, such as abnormal histological structures, immune cell infiltration, and lung edema were less severe following BJT treatment. BJT inhibited the LPS-induced increase of cytokines such as interleukin 4, 6, 10, and tumor necrosis factor alpha.
Conclusion
BJT had an inhibitory effect in the pathological progress of LPS-induced sepsis and ALI and may be a promising therapeutic agent in the future.
- Effectiveness of the Korean Medicine-Based Postnatal Healthcare Program: A Retrospective Observational Study
- Joohee Seo, Doeun Lee, Hansong Park, Inae Youn, Jungtae Leem, Minjung Park
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(2):117-125. Published online June 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.06.006
- 1,393 View
- 32 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- Background
Insufficient postpartum care can negatively affect mothers’ health. The aim of the Korean Medicine-based Postnatal Healthcare Program (KMPHP) is to prevent and treat Sanhupung by rapid intervention in postpartum care.
Methods
A retrospective study was conducted using data from 37 postpartum women who participated in the KMPHP between April 2019 and April 2020. The women had received at least one type of Korean medicine treatment (herbal medicine, acupuncture, electroacupuncture, pharmacoacupuncture, or Chuna manual therapy) for at least one session. General characteristics were collected from the medical records, and postpartum symptoms (taken from a questionnaire) were investigated. Outcome measures included pain intensity, quality of life (QoL), and postpartum depression.
Results
The effectiveness of the KMPHP was determined using the paired-sample Wilcoxon test and significant improvements in the scores were observed using the Korean version of the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (from 8 to 5, p < 0.01), EuroQol-5 Dimension-5L (from 0.82 to 0.83, p = 0.02), and EuroQol Visual Analog Scale (from 70 to 80, p < 0.01). The womens’ pain scores (Numeric Rating Scale) reduced from 4 to 3 after treatment, but the difference was not significant. As a result of analyzing the effects of each intervention, herbal medicine show a significant effect on womens’ depression, QoL and pain, and non-pharmacological intervention showed synergistic effects with herbal medicine.
Conclusion
Korean medicine-based interventions may be effective in the management of postpartum health by improving mothers’ emotional status, QoL, as well as reducing pain.
Short Communication
- The Mazzanti AcuOsteo Method®: Pathology and Treatment with Acupuncture and Osteopathy of the Musculoskeletal Pain of The Upper and Lower Limbs
- Umberto Mazzanti
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(2):126-130. Published online June 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.06.007
- 1,398 View
- 90 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Musculoskeletal pain is one of the most frequent reasons for consultations in my clinic. In my experience of 35 years, acupuncture, and osteopathy are effective techniques in the treatment of musculoskeletal pain of the upper and lower limbs. Pain reported by the patient often affects a widespread area around the joint and is usually associated with some stiffness. The aim of acupuncture is to restore the local circulation of Qì and Blood, inducing an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect, along with myofascial detensioning. The aim of the osteopathic manipulative treatment is to return joints to their normal position and restore restricted joint motion. The Mazzanti AcuOsteo Method is a newly patented method which uses the synergistic combination of using points for acupuncture, cupping or bleeding, and osteopathy to maximize effectiveness of treatment for musculoskeletal pain.
Protocols
- Systematic Review Protocol for Sham Acupuncture Validation Research
- Sung Min Lim
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(2):131-133. Published online June 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.06.008
- 698 View
- 8 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Background
Streitberger and Park sham needles have been developed and used as non-penetrating sham acupuncture needles that can be blinded in randomized controlled clinical trials assessing the efficacy of acupuncture. Ideal sham acupuncture should not be distinguishable from an actual acupuncture treatment provided to the experimental group to ensure patient blinding; additionally, it should not have any physiological or biological effect. Providing evidence for such sophisticated sham acupuncture devices is critical, as control settings in clinical studies are based on research verifying their validity.
Methods
Three core electronic databases - PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials - will be used to search for validity verification studies of sham acupuncture devices. Clinical studies that verify the validity of non-penetrating sham acupuncture devices will be included in the review.
Results
The study design, participant information, experimental and control groups, study population’s experience with acupuncture, outcome variables, and results of studies that verify the validity of sham acupuncture devices will be systematically reviewed.
Conclusion
This systematic review of validity verification studies of sham acupuncture devices is expected to help the development of more sophisticated sham acupuncture, as well as the design of studies verifying its validity in the future.
- Effectiveness and Safety of Duantengyimu-tang for Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Protocol for a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Gyoungeun Park, Jeong-Hyun Moon, Eun-Jung Kim, Won-Suk Sung
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(2):134-137. Published online June 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.06.009
- 742 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Per-oral pharmacological medication is a representative treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and has improved over several guidelines. However, limitations of long-term use of these medications including adverse events, led to the introduction and utilization of complementary and alternative treatments for RA. Several herbal medicine decoctions have been reported to be effective and safe; a recent study introduced Duantengyimu-tang (DTYMT). Regardless of the pharmacological effects of the DTYMT components, there are concerns about its safety. Therefore, this systematic review (SR) will focus on the effectiveness and safety of DTYMT treatment for RA.
Methods
Searches for randomized controlled trials using DTYMT treatment for RA will be performed using multiple electronic databases, manual searches, and emails (if necessary). A summary will be written using data on outcome measurements of the study participants, interventions, adverse events, and risk of bias in the studies. The primary outcomes will be disease activity scores including effective rate, tender joints, swollen joints, and morning stiffness. The secondary outcomes will include adverse events and blood tests for RA (erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, and rheumatoid factors). This SR will use Review Manager software to perform a meta-analysis, the Cochrane Collaboration “risk of bias” tool, and determine the quality of evidence using the Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation method.
Results
This SR will investigate the clinical effectiveness and safety of DTYMT treatment in patients with RA.
Conclusion
This SR aims to be informative for patients and clinicians in clinical practice, researchers, and policymakers in managing RA.





 First
First Prev
Prev


